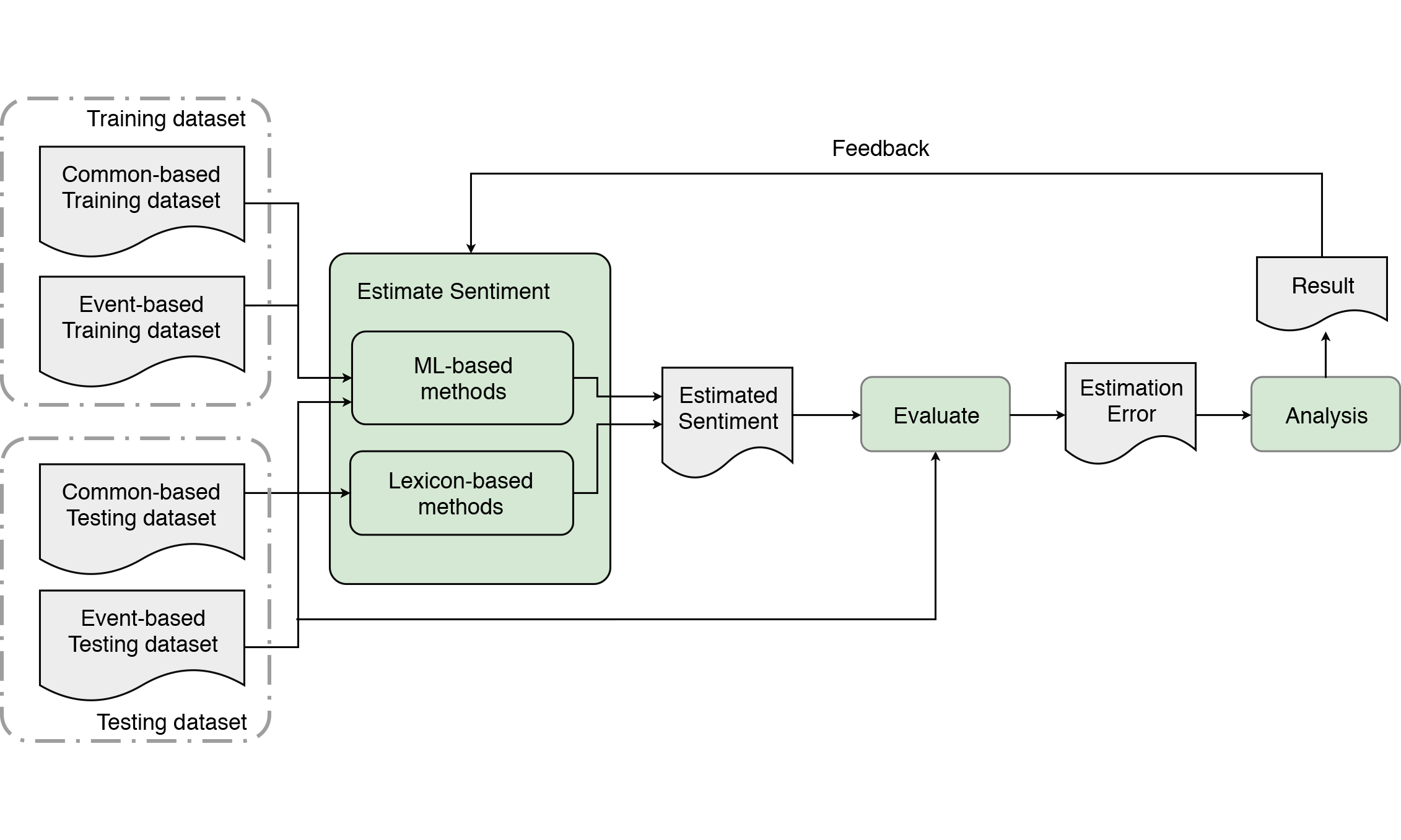
Estimate sentiment of crowds from social media during city events
For more detail please refer to the Link.
City events are becoming more frequently organized and more crowded in urban areas. There is an increased need for novel methods and tools that can provide sentiments of crowds as input for crowd management. Previous works explored sentiment analysis and proposed a large number of methods in various contexts. However, none of them aimed at deriving the sentiment of crowds using social media in city events, and no existing event-based dataset is available for such studies. In this work, we investigated how social media can be used to estimate the sentiment of crowds in city events. First, we selected some lexicon and machine learning methods to perform sentiment analyses. Then we constructed an event-based sentiment annotated dataset. We trained and tested the performance of the selected methods in an experiment using common and event-based datasets. Results show that the machine learning method Linear-SVC reaches the lowest estimation error for sentiment analysis on social media in city events. The proposed event-based dataset is essential for training methods to reduce estimation error in such contexts.
The research approach is illustrated in the following figure.